
8(903)201-21-74
ООО "ЧетыреДатчика"
 |
Оператор: 8(903)201-21-74 ООО "ЧетыреДатчика" |
|
Оператор: 8(903)201-21-74 ООО "ЧетыреДатчика" |
Главная страница Titan-nvr manual 1 ... 5 6 7 8 9 6. Remote PC System Requirements Remote PC Minimum Requirements
7. Troubleshooting 7.1 Replace a Failed Disk Drive If a disk drive fails, the Disk Status LED becomes orange. If the disk drive belongs to a RAID Volume, the Volume goes Critical or Offline, depending on RAID level. See Check RAID Volume Status for details. Replace the failed disk drive with a new disk drive of the same or slightly greater capacity. You do not have to power down the unit. Refer to Modify RAID Volume to remove the failed disk and replace it with a new one. 7.2 Respond to a Critical RAID Volume How the unit responding to a Critical RAID Volume depends on the RAID level of your Volume: For RAID 1, 5, and 10 volumes, you must replace the failed disk drive with a new one. The RAID Volume will begin rebuilding itself when you install the new disk drive. See Replace a Failed Disk Drive for details. RAID 0 volumes go offline after a disk drive failure. A RAID 0 Volume cannot be recovery. All data of the volume is lost. 7.3 Respond to a File System Error RAID Volume When encountering file system error, you are unable to keep the data anymore. Its likely due to abnormal usage and disk damage. In this case, if you want to keep recording, we suggest replacing new disks, or try the following methods. 1. Format this volume, and check if the status becomes functional. If yes, you can start recording. If it doesnt, try the second method. 2. Delete this volume, and create volume again to see if the status is functional. 7.4 Install ActiveX If you cannot see the complete page of the system when using Internet Explorer, it may be because the ActiveX installation process is not completed. 1. Log in to the unit. 2. Click the NuClient button on the top right. 3. The browser will ask whether to install ActiveX.  4. Click the Run button on popup dialog to begin the installation process. 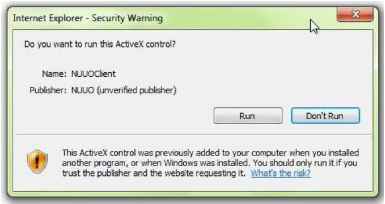 7.5 Cannot Log in to the Unit with Internet Explorer 1. Check the settings of your antivirus software. 2. Change to appropriate settings or turn off this antivirus software. Please visit NUUO wiki for more information. http: support.nuuo.com/mediawiki/index.php/Main Page Appendix - RAID System Introduction to RAID RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) allows multiple disk drives to be combined together into a RAID Volume. You will create a RAID Volume on your unit when you perform the setup procedure. The benefits of a RAID can include: Higher data transfer rates for increased server performance Increased overall storage capacity for a single Volume Data redundancy/fault tolerance for ensuring continuous system operation in the event of a disk drive failure Different RAID levels use different organizational models and have varying benefits. The following outline breaks down the properties for each RAID level supported on this unit: RAID 0 - Stripe When a RAID Volume is striped, the read and write blocks of data are interleaved between the sectors of multiple disk drives. Performance is increased, since the workload is balanced between drives or members that form the RAID Volume. Identical drives are recommended for performance as well as data storage efficiency. 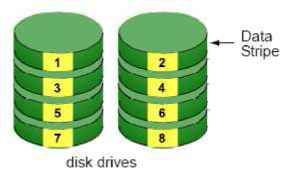 The RAID Volumes data capacity equals the capacity of the smallest disk drive times the number of disk drives. For example, one 100 GB and three 120 GB drives will form a 400 GB (4 x 100 GB) RAID Volume instead of 460 GB. If disk drives of different capacities are used, there will also be unused capacity on the larger drives. Because RAID 0 does not offer Fault Tolerance, meaning that you cannot recover your data after a disk drive failure, we do not recommend a RAID 0 Volume for your unit. RAID 0 Volumes on this unit consist of one or more disk drives. RAID 1 - Mirror When a RAID Volume is mirrored, identical data is written to a pair of disk drives, while reads are performed in parallel. The reads are performed using elevator seek and load balancing techniques where the workload is distributed in the most efficient manner. Whichever drive is not busy and is positioned closer to the data will be accessed first. With RAID 1, if one disk drive fails or has errors, the other mirrored disk drive continues to function. This is called Fault Tolerance. Moreover, if a spare disk drive is present, the spare drive will be used as the replacement drive and data will begin to be mirrored to it from the remaining good drive. 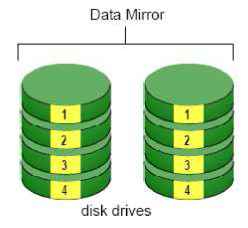 The RAID Volumes data capacity equals the smaller disk drive. For example, a 100 GB disk drive and a 120 GB disk drive have a combined capacity of 100 GB in a mirrored RAID Volume. If disk drives of different capacities are used, there will also be unused capacity on the larger drive. RAID 1 Volumes on this unit consist of two disk drives. If you want a mirrored RAID Volume with more than two disk drives, see RAID 10 - Mirror / Stripe for details. RAID 5 - Block Striping with Distributed Parity RAID 5 organizes block data and parity data across the disk drives. Generally, RAID level 5 tends to exhibit lower random write performance due to the heavy workload of parity recalculation for each I/O. RAID 5 works well for file, database, application and web servers. 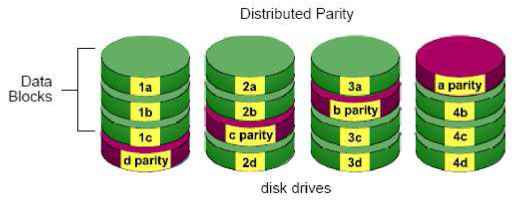 The capacity of a RAID 5 Volume equals the smallest disk drive times the number of disk drives, minus one. Hence, a RAID 5 Volume with four 100 GB disk drives will have a capacity of 300 GB. A RAID Volume with two 120 GB disk drives and one 100 GB disk drive will have a capacity of 200 GB. RAID 5 is generally considered to be the most versatile RAID level. RAID 5 requires a minimum of three disk drives. RAID 10 - Mirror / Stripe Mirror/Stripe combines both of the RAID 0 and RAID 1 types. RAID 10 can increase performance by reading and writing data in parallel while protecting data with duplication. At least four disk drives are needed for RAID 10 to be installed. With a four-disk-drive RAID Volume, one drive pair is mirrored together then striped over a second drive pair. 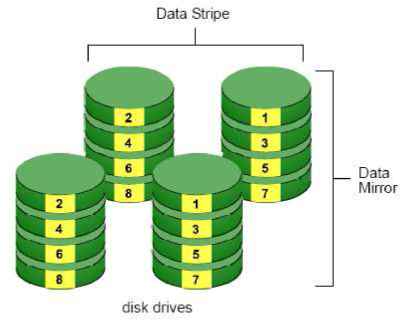 The data capacity RAID 10 Volume equals the capacity of the smallest disk drive times the number of disk drives, divided by two. In some cases, RAID 10 offers double fault tolerance, depending on which disk drives fail. RAID 10 Volumes on this unit consist of four disk drives. Because all of the available disk drives are used for the RAID Volume, you cannot set up a spare drive with RAID 10. Choosing a RAID Level There are several issues to consider when choosing the RAID level. The following summarizes some advantages, disadvantages and applications for each choice.
Appendix - Camera Integration Camera Supporting List Refer to NUUO website: http: www.nuuo.com/product.php?id = 12 Camera Search Tool ACTi Arecont Sony Stream Profile Original Low: under 300kbps; designed for mobile client single-view Minimum: under 100 kbps; designed for mobile client multi-view
1 ... 5 6 7 8 9 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||